
During the last 10 years, more and more electronic devices as well as security and fuel saving systems have found their way into modern buses. In combination with shorter routes and more frequent schedules, the battery is used 24 hours a day, seven days a week. This calls for new technologies in energy supply, as regular batteries cannot keep up anymore. Varta reports.
Ensuring the reliability of their bus fleets and maintaining low operating costs have become key factors for public transportation companies – whether on urban, inner-city, or long-distance routes. The latest bus models incorporate technology that requires a greater reliance on batteries to supply increased electrical loads to operate components and accessories such as Wi-Fi, cameras, payment systems and air conditioning. Furthermore, ticketing machines and infotainment systems must be updated each night. These new electrical systems demand a much higher energy than traditional flooded batteries are able to provide as they are not designed for deep cycling – a capability only AGM technology can provide.
What is AGM technology?
AGM stands for Absorbent Glass Mat. The glass mat fleece soaks up the acid in the battery like a sponge, providing the highest possible cyclic stability and extreme vibration resistance. Since there is no acid stratification, overall capacity loss is reduced to a minimum, resulting in a much longer life compared to conventional batteries.
Cycle life is a crucial performance indicator in energy demanding applications. It defines how many times a battery can be discharged and recharged before it reaches its end of life. Leading proprietary AGM batteries can stand six times more cycles compared to conventional batteries.
With its cycling stability and depth of discharge capabilities, AGM is the perfect technology for buses that need to supply electrical consumers around the clock.
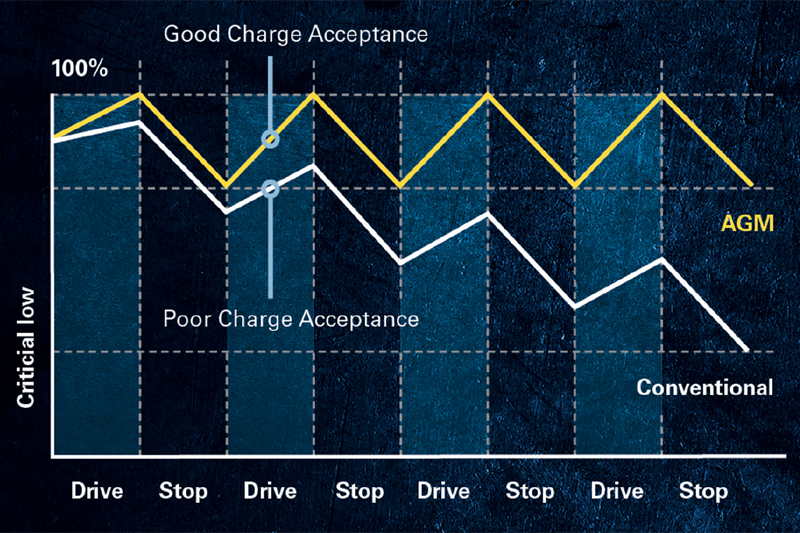
Public transport companies are planning their routes more effectively today. To provide as much mobility as possible to the customers, more stops are added. Punctuality is another important factor. Even short delays can lead to customer dissatisfaction, penalties, and therefore high efforts for bus fleets. Shorter driving times save fuel, emissions, and noise, but for the battery this also means much shorter charging times. In addition, accessibility features like ‘kneeling’ mechanisms need to be powered to help wheelchair users, passengers with strollers and people with reduced mobility board. This can lead to a negative charging balance with conventional batteries and therefore to battery breakdowns.
With the use of AGM technology and its much better charge acceptance, the energy balance is kept positive. Furthermore, AGM technology makes sure that the battery has a high state-of- charge at the end of the day which reduces additional recharging and cost.
Saving fuel is hard work for the battery
Due to governmental regulations, commercial vehicle manufacturers in the EU must reduce their fleets’ CO2 emissions to 15% by 2025 and 30% by 2030. New energy saving functions are being installed to meet these regulations.
Fuel saving systems like passive boost, start-stop and eco-roll all provide some form of downtime for the engine. For instance, eco- roll is a function in vehicles with predictive cruise control which calculates fuel saving effects depending on the topography of the route. In areas with small declines the engine is running in idling mode to save fuel. The battery is not being charged during these periods. While the alternator is having a break, electrical devices like GPS, air conditioning, mirror cams, info screens and Wi-Fi continue to discharge the battery. Having to support electronic and electrical devices for improving driving efficiency, safety and comfort puts additional strain on the battery.
Here the charging capabilities play a major role. As leading proprietary AGM batteries need to be charged less overall and recharge much faster, they provide a higher charge acceptance than conventional batteries.
The integration of electric or hybrid buses to reduce pollution and noise emission in inner cities is increasing. And while propulsion is handled by a high-voltage battery, these vehicles all rely on 24V batteries to power their electrical system.
In full-electric vehicles, 24V AGM batteries play a major role in regard to the functional safety by supplying the vehicle’s electrical system. They secure functions like lights, brakes, steering and systems in the vehicle, even during an outage of the high-voltage-system. Charged 24V batteries are also mandatory for starting the electric power train.
Original equipment manufacturers have been working for a long time on developments in the area of full electric heavy commercial vehicles. The main focus of the OEs and the fleets is to get as much operating distance as possible from the electric power unit. That means that energy for safety and comfort functions will be provided by AGM technology.
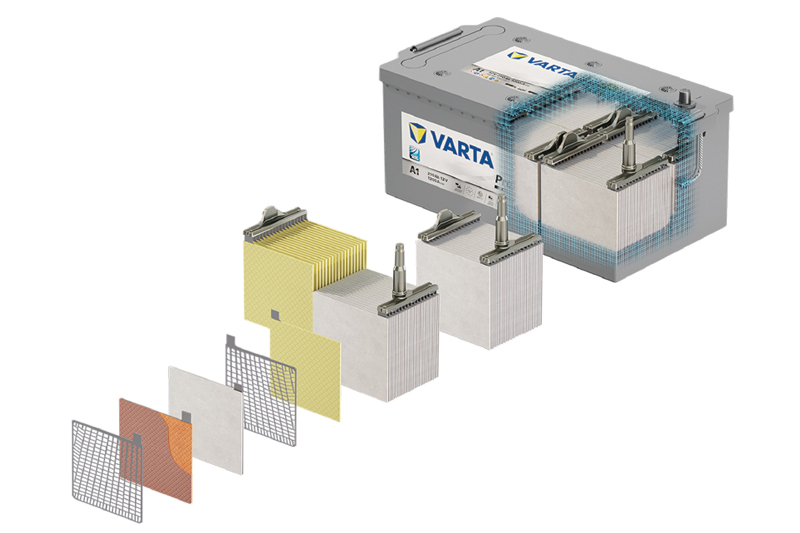
VARTA ProMotive AGM
A unique feature of VARTA AGM batteries is the patented PowerFrame® design. The VARTA ProMotive AGM is the first battery to use this special grid on both the positive and negative plates for optimum performance and excellent starting characteristics even at low charge levels.
Due to the special design of the VARTA ProMotive AGM, up to 80% of the specified capacity can be utilized without significantly compromising cycle life, which is a key requirement for well- equipped buses. In comparison, the recommended depth of discharge (DOD) of a regular starter battery is 20%.








