How do NOx sensors work?

Everything you need to know about how NOx sensors work from febi.
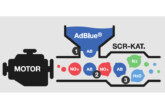
In order to meet the high requirements of the current emission standards, the proportion of harmful nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gas must be reduced, among other things. This is achieved by a chemical process that uses a reduction agent to selectively reduce the nitrogen oxides NOx in the exhaust gas by removing oxygen. NOx is a collective term for the nitrogen oxides nitrogen monoxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) and other nitrous gases.

The chemical process for reducing nitrogen oxides is called selective catalytic reduction (SCR). Ammonia NH₃ has proven to be the best reducing agent, because it achieves the highest selectivity.
The ammonia is carried in the form of a urea-water solution, also known as AdBlue, in a separate tank. The urea-water solution is injected into the exhaust system where it is converted into ammonia by the high temperature of the exhaust gas and in a hydrolysis catalytic converter. Subsequently, the harmful nitrogen oxides are reduced to harmless nitrogen and water in the SCR catalytic converter.
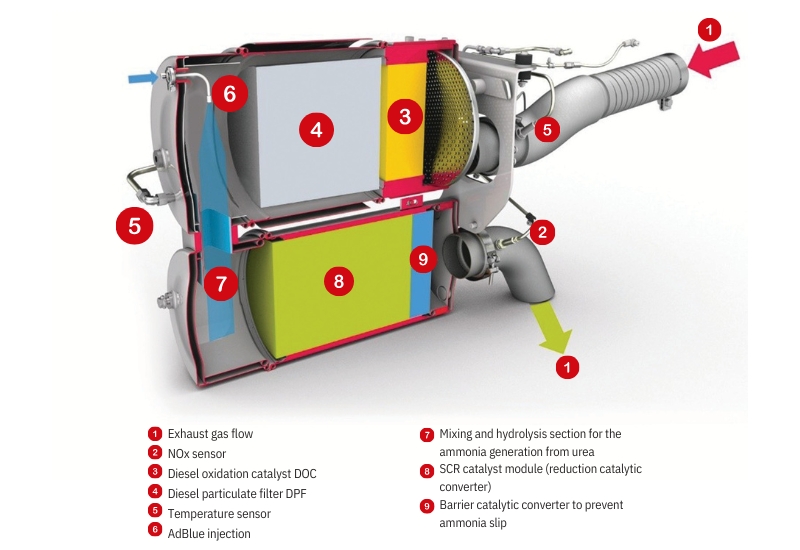
To monitor the reduction process, current vehicles are equipped with either one NOx sensor (nitrogen oxide sensor) downstream of the SCR catalytic converter or two NOx sensors, one upstream and one downstream of the SCR catalytic converter. They monitor the function and effectiveness of the SCR system by measuring the nitrogen and oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. The data from the NOx sensors is also used to calculate the amount of AdBlue required for an optimal reduction process.
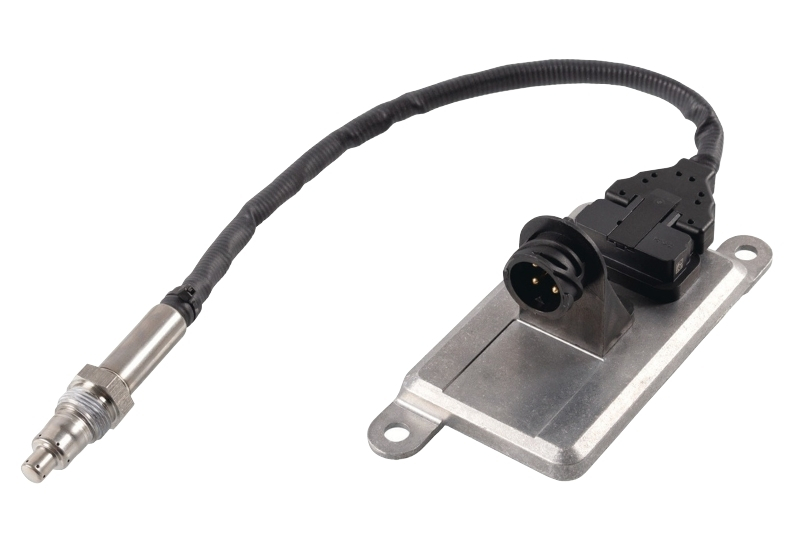
A NOx sensor consists of a probe (1), a connection cable (2), a control module (3) and a connector plug (4).
The measuring principle
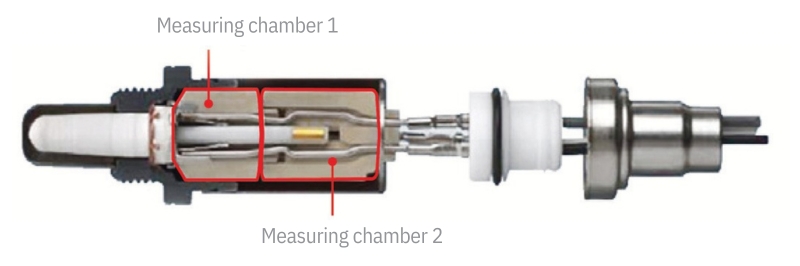
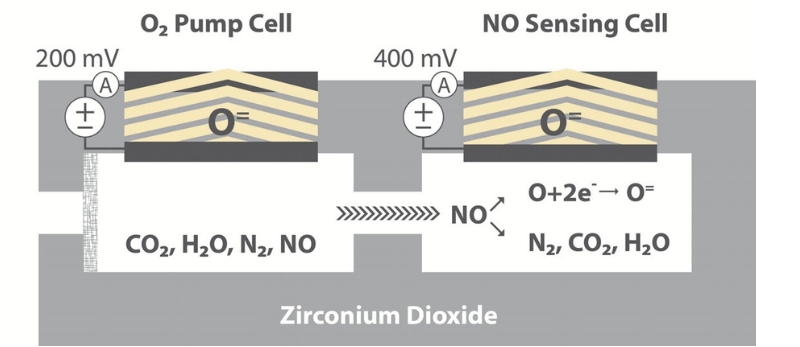
Current NOx measurement technology is based on electrochemical sensors with yttrium-stabilised zirconium dioxide ZrO₂, whose design and mode of operation is similar to broadband oxygen sensors (lambda sensors). The sensor usually uses two adjacent measuring chambers with two electrochemical cells, also called pump cells.
The exhaust gas flows into the first chamber, where oxygen (O₂) is removed electrochemically. This is necessary because otherwise the nitrogen oxide measurement in the second chamber would be affected. With the help of an electrical voltage applied to the pump cell, the O₂ molecules are broken down into ions. They penetrate the solid electrolyte consisting of zirconium dioxide and are thus removed from the measuring chamber.
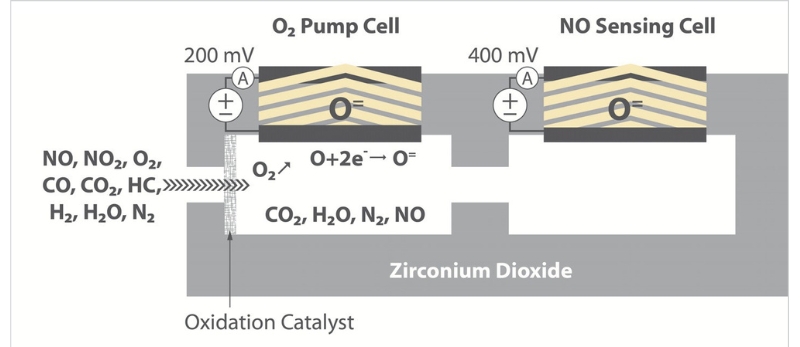
The electrical power that has to be applied for this is inversely proportional to the air-fuel ratio. This value is also made available to the engine control unit, which then additionally fulfils the function of a lambda probe for measuring the oxygen content in the exhaust gas.
In the second chamber, the NOx content in the exhaust gas is determined. For this purpose, the remaining nitrogen oxide NOx is reduced to nitrogen and oxygen by the catalytic material of a platinum-rhodium electrode. The oxygen produced is then pumped out of the measuring chamber through this electrode. To achieve this, a current flows through the electrode that is proportional to the concentration of nitrogen oxide NOx in the exhaust gas. It is precisely this necessary pumping current that is the measurand for the NOx content in the exhaust gas.
This is then used to calculate whether the NOx storage catalytic converter needs to be regenerated, the AdBlue injection quantity needs to be adjusted and whether the SCR system is functioning correctly at all.
In current vehicles that meet high exhaust emission standards, the exhaust gas management is monitored in real time. The AdBlue level, quality and consumption as well as the injection system and the NOx values are permanently monitored. In the event of a defect in the SCR system or deviations from the target values, warnings are sent to the driver. If the driver does not react, the engine output is reduced according to the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications. In the worst case, the driver can only drive at walking speed to the next workshop.

Reliability
NOx sensors have a limited lifetime. Due to ageing of the materials in the sensor, the reliability of the measurements decreases after a certain time and the driver receives an error message. Rely on febi‘s NOx sensors in the usual high original equipment quality. In addition to NOx sensors, febi also offers many other spare parts for SCR systems, such as AdBlue fluid, the corresponding filters and tank caps, metering modules and exhaust gas temperature sensors.