
CVW learns how Knorr-Bremse’s Aldersbach plant transforms a brake caliper blank and a few dozen other components into the complete product.
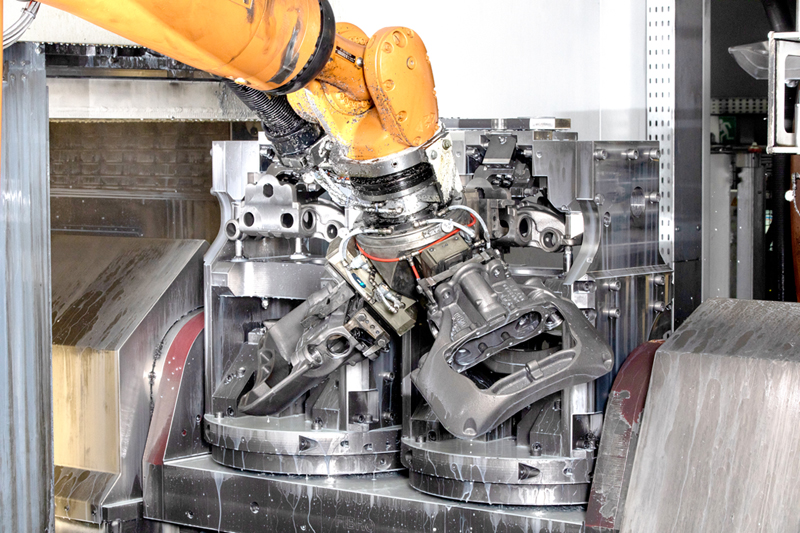
Step 1. Caliper processing

The operator first loads the caliper blanks on to one of the electronic machining units before handing over control to the machine, which automatically turns, drills, mills and grinds each blank until it starts to look like a complete brake caliper.
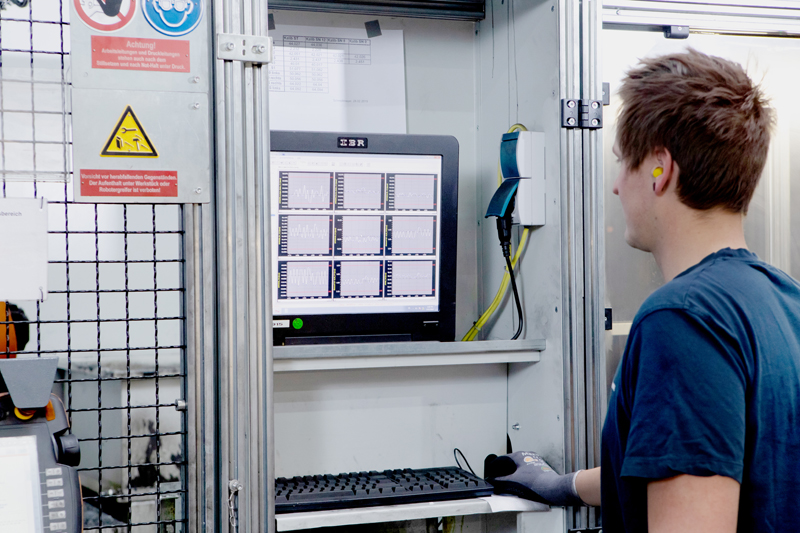
Step 2. 3D Measurement of the brake caliper
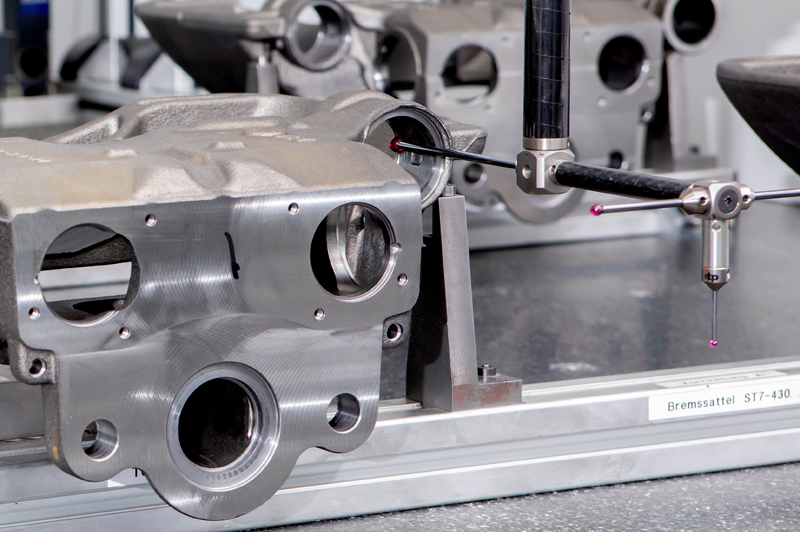
3D measurement is carried out either directly on the machining unit or in a high-tech metrology room. This enables the results of the machining process and the surface of the brake caliper to be examined. The resulting log data also enables the operator to check that the machining unit is functioning properly. Correctly machined brake calipers are then immersed in an electroplating bath to increase corrosion resistance.
Step 3. Slack adjuster assembly
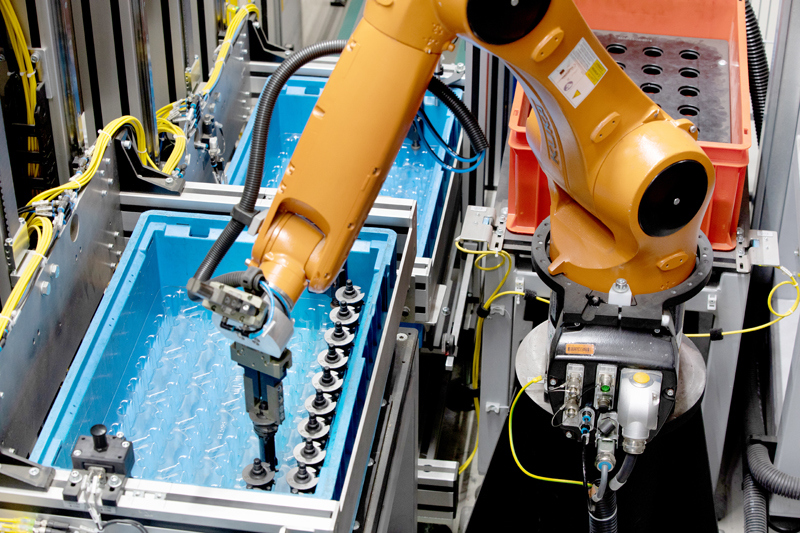
The mechanical slack adjusters ensure maximum braking power and short brake reaction times. In 49 process steps, the slack adjusters are assembled and small quantities of grease are applied to their bearings. They are then pre-loaded and sealed before being fitted to the disc brake. During assembly of the slack adjusters, laser testing is carried out, as well as pressure distribution and camera checks, followed by a final inspection.
Step 4. Brake assembly
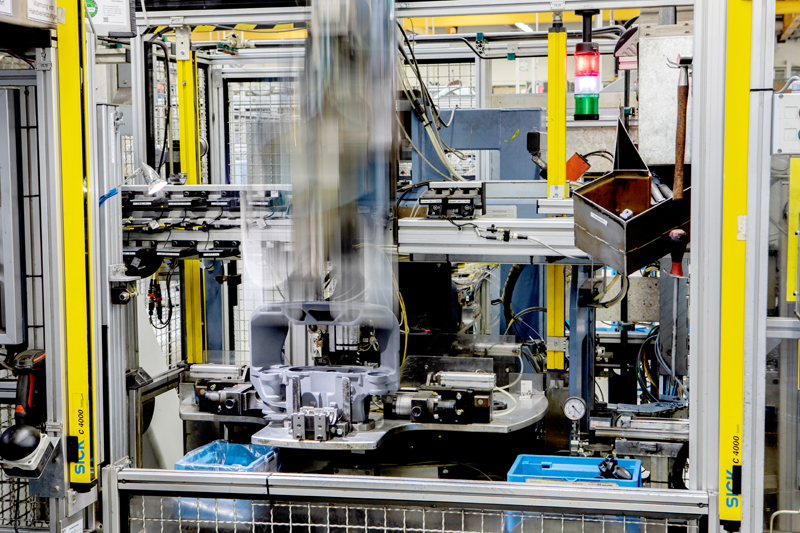
Depending on the type, a disc brake can consist of between 45 and 50 components. Assembly starts with the internal mechanical components. At the first of many workstations, the brake lever and mounting bracket are automatically added. The process is a mixture of manual and automated work, with human operatives working at four of the workstations, and the rest of the assembly and inspection carried out by robots.
Step 5. Functional testing
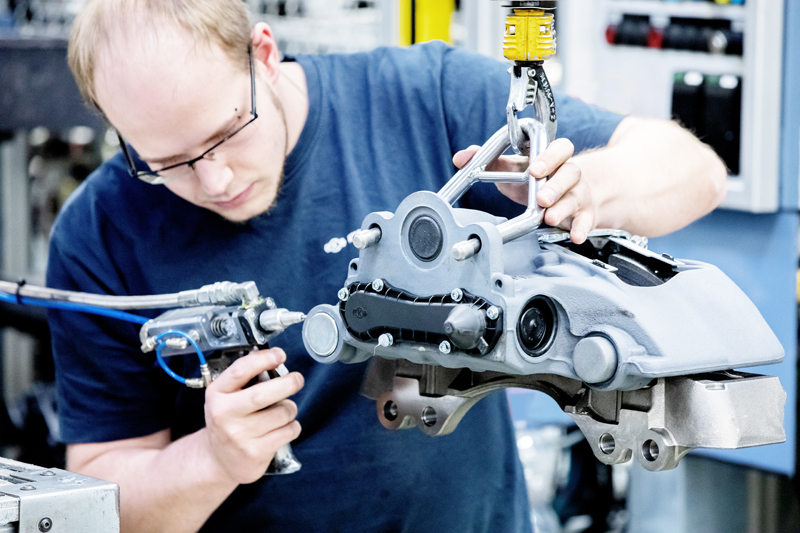
The assembled disc brakes are only released once all their functions have been successfully tested. The last stage of this process is the camera test, involving a final visual check to ensure that all parts of the disc brake have been correctly assembled. After a final examination of all the data relating to the assembly process, the brake, complete with its type plate and bar code label, is released for delivery to the customer.








