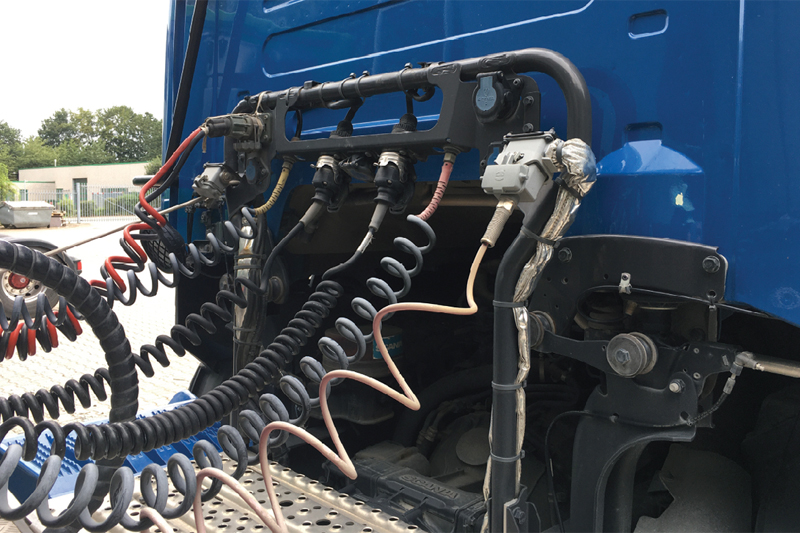

Ensuring the electrical coils have a safe and flexible connection between the trailer and towing vehicle is of paramount importance. febi explains everything you need to know.
Electrical coils are necessary to provide a flexible connection between the electric and electronic systems of the trailer and the towing vehicle. Not only does this include the lighting of the trailer, but also tail lifts and other electrical components are supplied with power by the towing vehicle. The ABS or EBS system must also communicate signals with the towing vehicle via the data bus system. For all these systems to function correctly, they need a secure connection.
What to know
While the distance between the electrical coil connections between the cab and trailer is relatively small when driving straight ahead, the situation is quite different when driving around curves. This is because the towing vehicle swings out strongly in tight curves and the coils are therefore stretched. Different coil lengths are required depending on the type of vehicle. A distinction is made between the working length of the spirals and the maximum length. Ideally, the maximum distance corresponds approximately to the working length of the coil. Under no circumstances should the maximum working length be exceeded, otherwise the coil may be damaged. Without a functioning electrical connection to the trailer, it is not possible to continue the journey for the time being.
In order to check the quality of replacement parts in the market, more than just febi products are regularly examined at febi. Since most defects in electrical coils are caused by plug connections, we have taken a closer look at them. In addition, the mechanical load capacity, which is relevant for practical applications, was also examined.
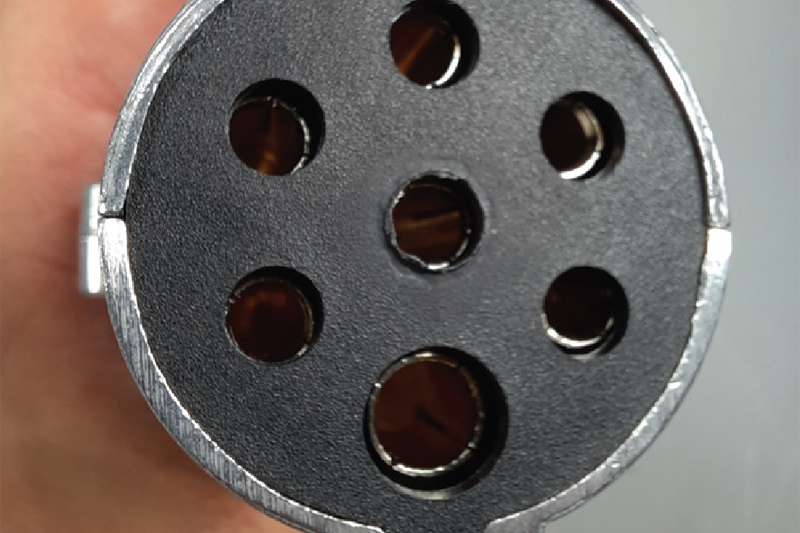

Plugs
The connection points of electrical circuits are the most common sources of error in electrical coils. Poor contact due to loose contacts or moisture are typically the causes. Sometimes the quality can already be seen in the processing of the plug:
Poor processing of the connector housing can lead to insufficient fitting accuracy and problems when inserting the connector. The position of the contacts is not optimal. They can be damaged by the mating part of the socket or pressed backwards out of the plug. Inserting the plug can be problematic if the contacts collide (Fig. 1).
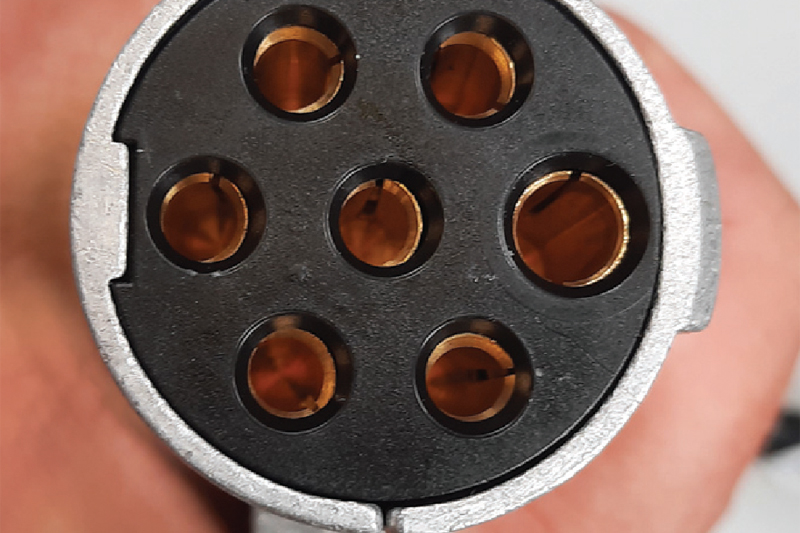

The febi plug (Fig. 2) is well manufactured and offers an optimal fit. The contacts are in the correct position so that plugging in the connector is easy.
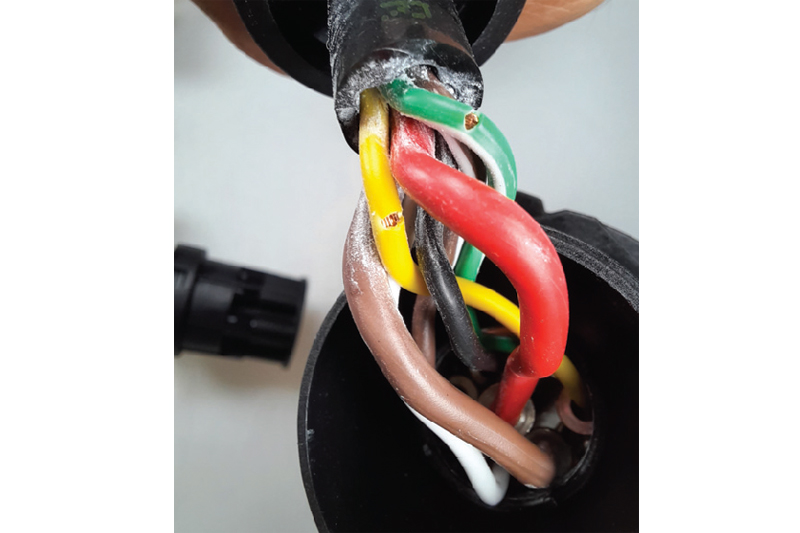

Mistakes can already be made during production. Here, you can see the damaged insulation of the cables of a new plug (Fig. 3). This can lead to short circuits that disable the electrical system. The cables of the febi plug are properly processed and show no signs of damage (Fig. 4).
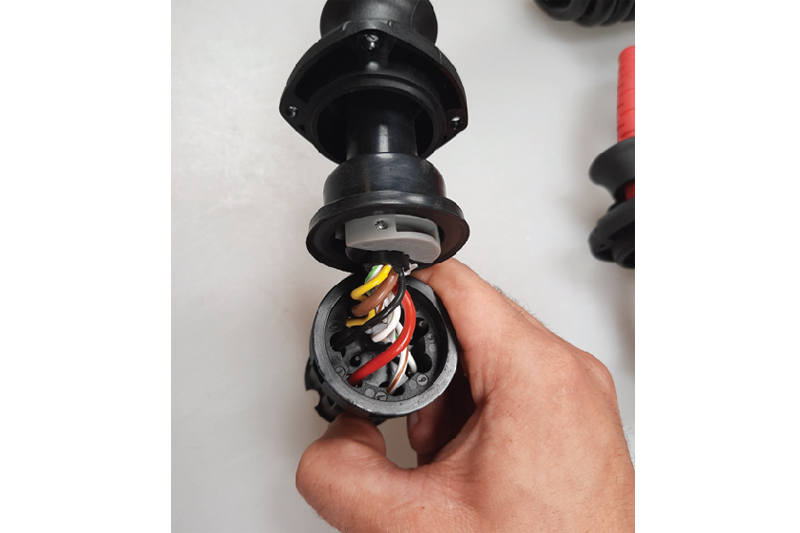

The kink protector of the plug should be stable and firmly connected to the plug and give the cable support. In this case (Fig. 5), the kink protector can be pulled out of the plug by hand and the cable is not sufficiently protected by the soft material. Both of these factors severely limit the service life.

The kink protection of the febi plug (Fig. 6) is firmly attached to the housing and cannot be pulled out. It is stable, gives the cable a good stability, and protects it.

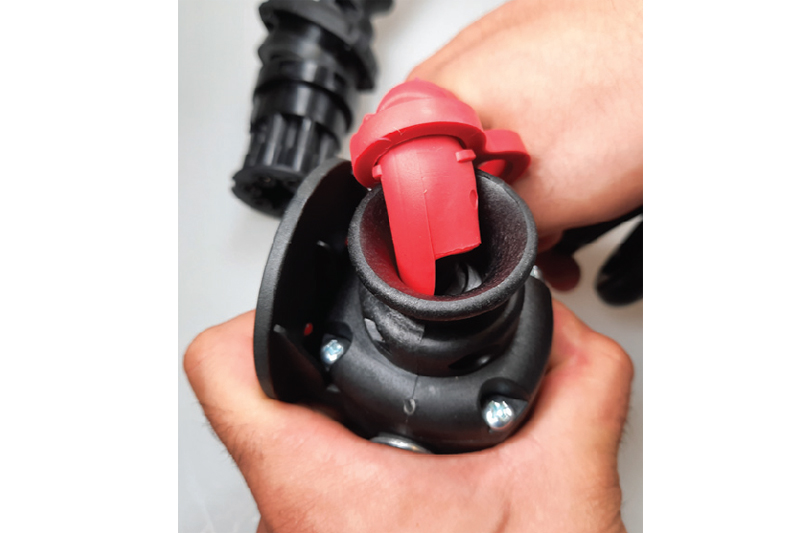
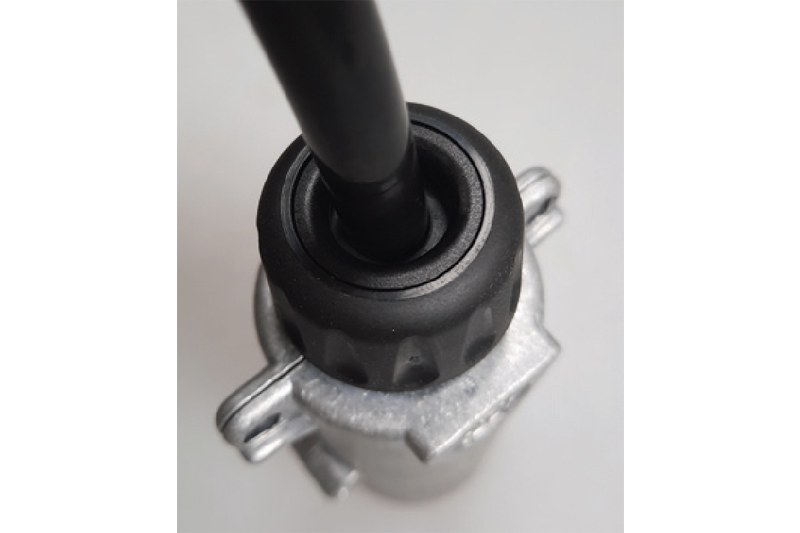
If the sealing of the cable to the plug is poorly constructed, moisture can penetrate the plug. Corrosion can then occur, which in turn can lead to poor electrical contact. Here, you can see the overly large gap between the cable and the seal, through which water can penetrate (Fig. 7).

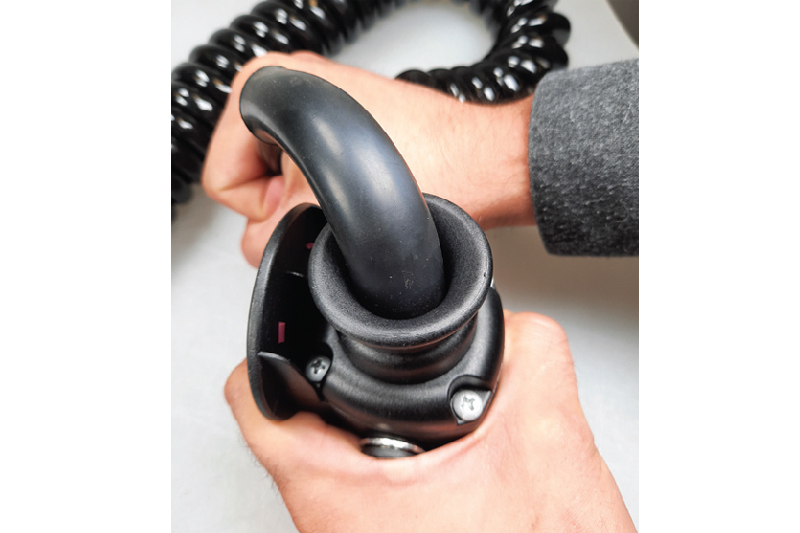
If special requirements are placed on waterproofness, febi offers a plug for retrofitting (Fig.8). It has a screwed seal which presses the sealing rubber firmly against the cable and effectively seals the plug.

In addition to these possible differences in quality, other aspects also play a major role when it comes to durability and safe functioning. For example, in the case of very inexpensive electric coils, cables with wire cross-sections that are too small are sometimes used. This is because the expensive copper in the cables is a cost factor.
However, a wire cross-section that is too small can lead to the heating of the cables when the current flow is high. If the cable becomes extremely hot, the insulation can melt and cause a short circuit. Sometimes, savings are also made on the processing of the contacts in the connector. A poor connection between the contact and the cable can quickly lead to problems in the electrical system, which can result in timeconsuming troubleshooting.
Tensile test
In order to check the mechanical load capacity of electrical coils, tensile tests were carried out on state-of-the-art test equipment. The force at which the cable is pulled out of the plug was measured. The 15-pole and seven-pole electrical coils were compared. In each case, the febi product and two competitive samples were put to the test.
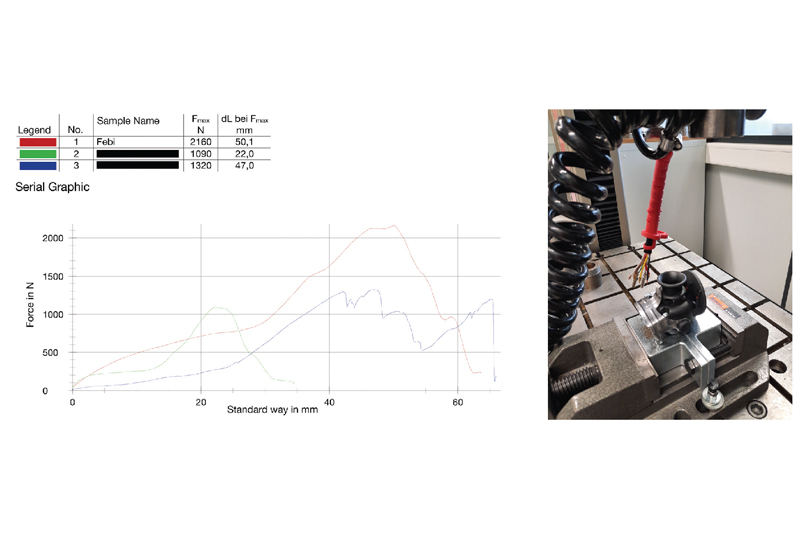
The strain relief in the 15-pole coils plug already gave way at 1090N and 1320N in the competition samples. The febi electrical coil withstood tensile forces up to 2160N (Fig. 9). The deviation of the tensile forces of the seven-pole coils is not as large as with the 15- pole coils, since the connection between plug and cable held for all test candidates. In the end, the weak point was the cable, which withstood 1703N and 1930N in the competition samples. The cable of the febi electric coil only broke at over 2000N (Fig. 10).
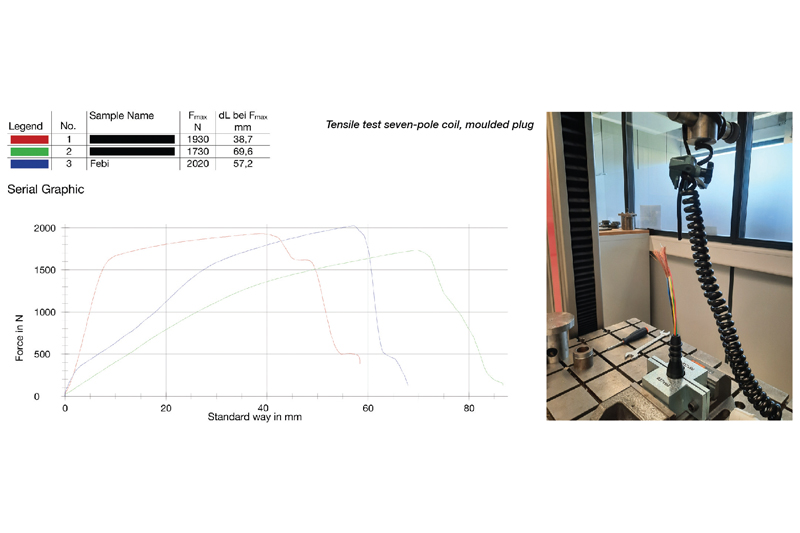
A closer look at the construction and processing of the various electrical coils will explain the results of the tensile tests. The high mechanical load capacity of febi electrical coils is due to the well thought-out design of the plugs and the quality of the production and the components used. In practice, all these factors put together ensure a permanently reliable electrical connection.
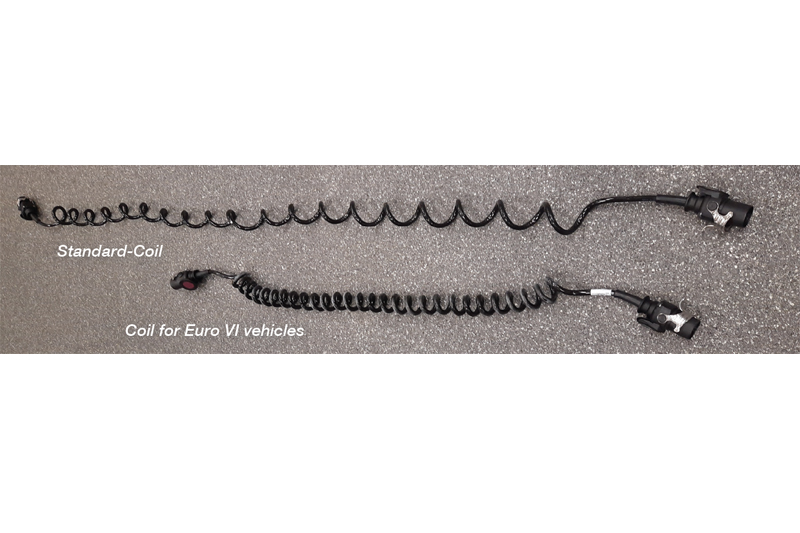
Electric coils specific to Euro VI vehicles
Vehicles that meet the Euro VI emission standard are very efficiently designed. The engine and its surroundings have a modern thermal management system, which ensures smart control of the water pump and cooling water temperature. Also, the air flow of the engine waste heat has been optimized.
For example, when driving slowly in traffic jams or in the city in combination with high outside temperatures, the air temperature in the area between the driver‘s cab and trailer can rise to as much as 125°C due to heat waste from the engine.
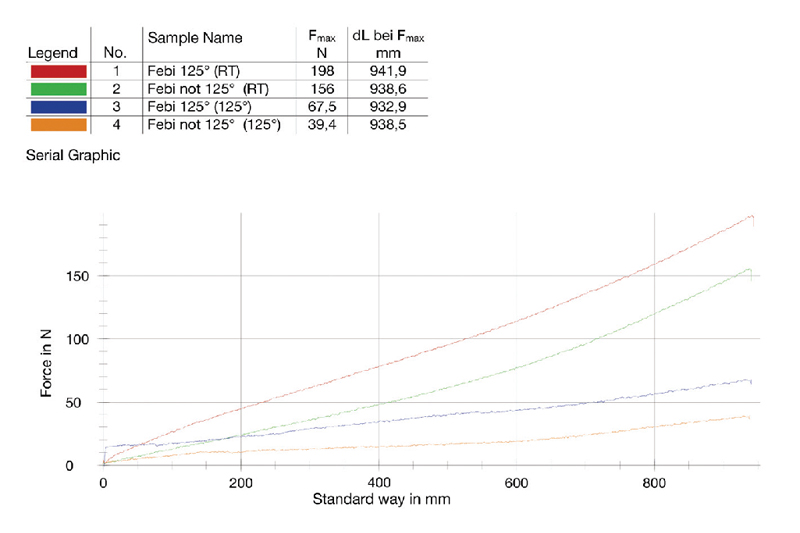
For this reason, there are electrical coils that can withstand these temperatures without damage. We conducted a test and compared a coil that is suitable for temperatures of 125°C with a standard coil (Fig. 11). For both coils, the restoring force was measured at room temperature (RT) and when heated up to 125°C.
It can be seen that even at room temperature, the 125°C coil has a higher restoring force than the standard coil. When the coils are heated up to 125°C, the restoring force of both coils decreases considerably. However, the 125°C coil has a more than 40% higher restoring force in the heated state compared to the standard coil.

The following picture (Fig. 12) shows the dimensional stability of both coils after the tensile test in the heated state.
The 125°C coil still has sufficient restoring force to retract. The coil, which is not heat-resistant, remains elongated and cannot be used any further, as it will sag and could come into contact with other vehicle parts. The result of the tensile test clearly shows that Euro VI vehicles should definitely be equipped with heat-resistant electrical coils. febi Truck offers a comprehensive range of electrical coils, plugs, sockets, and adapters in OE-matching quality for all common applications in the commercial vehicle sector.








